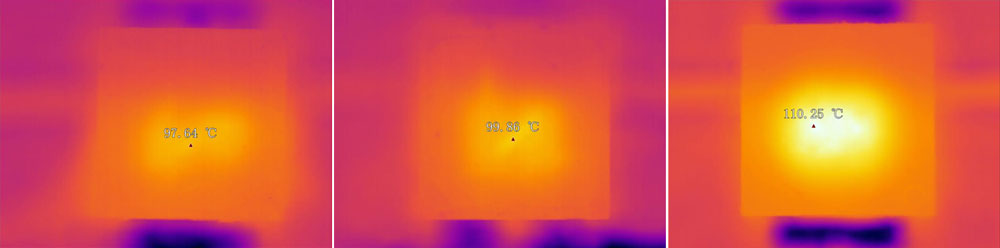
Le installazioni high bay solitamente hanno l'illuminazione al soffitto o in prossimità di esso. Per fornire un'illuminazione adeguata, queste lampade utilizzano in genere LED ad alta potenza . L'intensità luminosa emessa da un LED dipende dalla quantità di corrente fornita al LED e dalla temperatura di esercizio del LED. I LED che producono un flusso luminoso elevato possono essere azionati da segnali di azionamento elettrico elevati, che spesso determinano il funzionamento dei LED a temperature elevate. Inoltre, le applicazioni high bay in genere hanno ambienti più difficili e corrosivi rispetto alle applicazioni low bay. Soprattutto in stabilimenti di produzione come acciaierie, fonderie e vetrerie, gli ambienti high bay possono avere temperature ambiente più elevate e più particelle di polvere e olio. Quando si opera in ambienti con temperature ambiente elevate e/o in involucri con spazio limitato, il calore generato dal LED e dai relativi circuiti associati può danneggiare il LED.
1. Le alte temperature sono il più grande acceleratore di guasti quando si tratta di illuminazione a LED. La gestione termica delle lampade a incandescenza, fluorescenti e a ioduri metallici non è mai stata considerata in fase di progettazione. I LED, tuttavia, hanno un problema in quanto l'energia elettrica che non viene convertita in fotoni viene convertita in calore. In parole povere, i LED generano calore durante il funzionamento e i due non si mescolano bene insieme. A loro volta, i LED perdono molta della loro efficienza a causa del calore.
2. Negli ambienti ad alta temperatura sono presenti numerose sostanze volatili che risultano corrosive per i prodotti.
3. L'illuminazione ad alta temperatura per baie alte è generalmente installata a un'altezza particolarmente elevata e la manutenzione è particolarmente scarsa
Come dovremmo scegliere la nostra illuminazione industriale ad alta temperatura (High bay)?
1. Dovremmo fare un buon lavoro nella gestione termica dei diodi ad emissione luminosa
LEDRHYTHM N Azienda L Azienda
2.Il il materiale del dissipatore di calore deve essere LM6 o AlSi12
3. L' unità LED deve avere una protezione dello spazio indipendente
4.Resistenza al sovraccarico: 380 VAC , 48 h (supporta picchi di tensione < 4 kV)

Copyright © LEDRHYTHM Optronic Technology (Suzhou) Co., Ltd. Tutti i diritti riservati
Mappa del sito